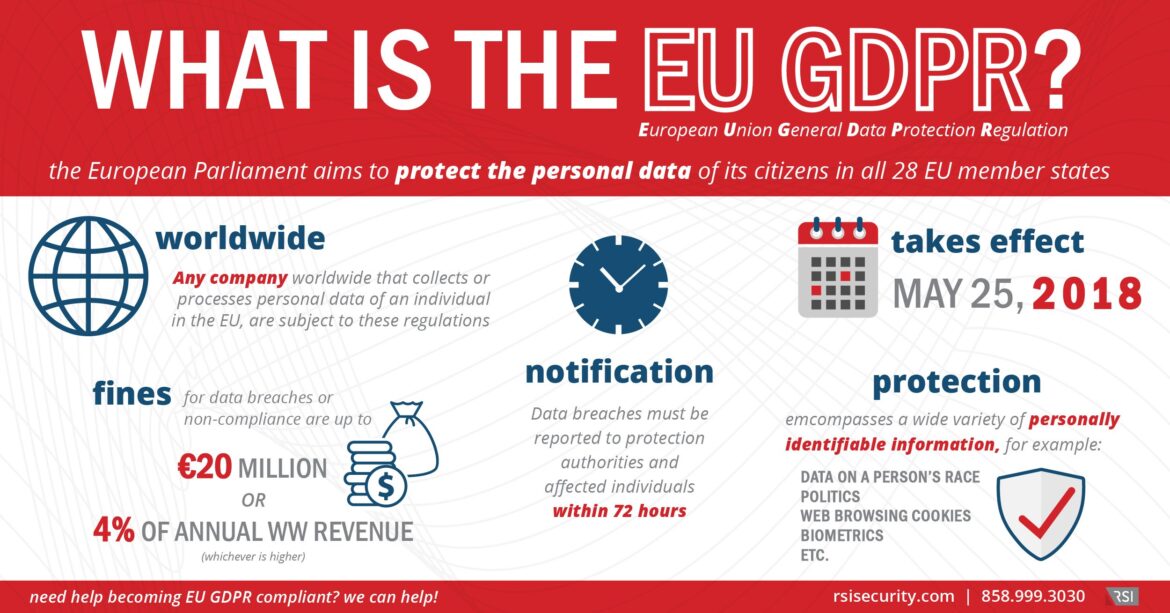
The impending European Union General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) represents a sea-change in a company’s security strategies, transcending checkbox compliance programs.
GDPR
What is the Purpose of a PIA? Considerations for GDPR Compliance
Privacy Impact Assessments (PIAs) exist to illustrate potential risks to GDPR data subjects’ privacy. They include information about data being collected, processes used, and risks involved. You may need to generate one if you work with the personal data of EU residents.
Is your organization working towards GDPR compliance? Request a consultation today!
What is the Purpose of a Privacy Impact Assessment (PIA)?
General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) compliance ensures the privacy of EU residents by safeguarding data belonging to them. One way that the GDPR protects data subjects is by requiring Data Protection Impact Assessments (DPIA), also known as Privacy Impact Assessments (PIA). They’re detailed reports on processes applied to data, and they illustrate the potential impact of said processing on the data subjects’ privacy.
Fully comprehending the purpose of PIAs requires understanding:
- What a PIA is (and what components are required at a minimum)
- When they are required (what circumstances necessitate them)
- How to conduct a PIA (and maintain GDPR compliance)
Working with a security program advisor will help your organization stay on top of its PIA needs.
What is a Data Protection Impact Assessment (DPIA)?
The terms “Data Protection Impact Assessment” (DPIA) and “Privacy Impact Assessment” (PIA) are used interchangeably in the GDPR. They both refer to tests organizations need to run to predict the possible impact of data processing on data subjects’ privacy. They document granular details about the data itself, the processes it will be subject to, and any possible risks.
In particular, a PIA should contain the following, at minimum, per GDPR Article 35(7):
- A description of all processes intended for the data, including their purpose(s)
- An analysis of how necessary all processes are, relative to said purpose(s)
- An analysis of the risks that said processes impose on data subjects’ rights
- A description of measures in place to prevent and mitigate any risks identified
These factors all need to be analyzed and documented prior to the data being processed—or collected for a given purpose. Another critical element of GDPR compliance is transparency, notifying data subjects of the potential impacts of data processing prior to collecting it.
Request a Consultation
When Do You Need a GDPR PIA or DPIA?
If your organization is processing personal information that belongs to GDPR data subjects, and there are risks that could jeopardize those subjects’ privacy, you may need a PIA. The more sensitive the data in question, or the greater the risk to it, the more likely it is that you need one.
In particular, Article 35(3) of the GDPR specifies three conditions under which a PIA is needed:
- If there are judgments being made on the basis of automated processing, especially if those judgments concern personal details or could inform legal or monetary outcomes
- If large amounts of data related to special categories detailed in Article 9 (e.g., data on subjects’ sexual identity, etc.) or Article 10 (i.e., criminal history) are being processed
- If large amounts of publicly available data are being processed in a systematic fashion
These are not exhaustive conditions; even if these are not met, a PIA may still be needed.
Ultimately, a DPIA or PIA assessment may be required if the amount or kind of personal data you’re working with or the processes being applied to it entail a significant amount of risk.

How to Conduct a PIA for GDPR Compliance
The method for conducting a PIA can vary depending on the kinds of data you’re working with, the processes intended for it, and the maturity of your security and compliance infrastructure.
First, you’ll need to scope. Gather as much information as possible on the data that is or will be collected, as well as the processes that have or will be conducted, and any risks entailed. This will help determine whether a PIA or DPIA is needed. It’ll also form the basis of your report.
Then, you can begin the process of analyzing the factors collected and reporting on the risks to GDPR data subjects. Generally, your analysis will start with vulnerabilities, which are gaps and weaknesses in your data environment that can be exploited by threats (e.g., cybercriminals). Together, the likelihood of exploitation and its potential impact are expressed as risk.
Depending on your findings, you may need to notify data subjects or GDPR authorities—or both. For example, if unanticipated risks are unearthed, data processes that had been deemed compliant may now need additional clearance or consent from impacted parties to remain so.
Throughout the process, it may be beneficial to work with a GDPR compliance advisor.
Optimize Your PIA Data Privacy Practices Today
To return to the question above: what is the purpose of a PIA? They exist to document potential risks to data privacy for GDPR-protected data subjects. Organizations are required to generate them in cases where the amount or kind of data being processed, or the processes being used, could amount to greater risks for the data subject. PIAs need to include, at minimum, specific details about the data being collected, the processes being performed on it, and their risks.
While the purpose and concept behind PIAs are relatively straightforward, the process of conducting one can be complex and challenging. RSI Security is committed to streamlining it.
Contact RSI Security today to learn how we can support your organization’s GDPR compliance.
GDPR Standard Contractual Clauses: Everything You Need to Know
TL;DR — The EU has a new set of Standard Contractual Clauses (SCCs) that are required for data transfers concerning protected personal information. In 2023 and beyond, you’ll need to incorporate intra-EU or international SCCs to ensure your data transactions are compliant.
Safeguarding data privacy is essential to becoming and remaining compliant with the GDPR. Using a GDPR privacy policy checklist, you can keep track of the types of data that require protection. This checklist also streamlines GDPR compliance year-round. Read our blog to learn about the GDPR privacy policy requirements.
Data privacy safeguards are critical to protecting sensitive GDPR data from privacy and security threats. One of the safeguards specific to the EU GDPR is the standard contractual clause (SSC), which outlines essential protections for data processors and controllers to follow when handling protected types of information. Read on to learn more about how the SSC works.
If your organization conducts business with other businesses, you may be wondering: how does GDPR affect B2B sales? GDPR may apply to different processes along the marketing and sales pipeline, depending on the type of transactions you conduct. Read on to learn more about remaining compliant with the GDPR as you engage in business-to-business transactions.
GDPR vs HIPAA Compliance: What are the Differences & Similarities?
Recent cyberattacks in the healthcare industry underscore the need for organizations to safeguard data privacy and sensitivity via HIPAA compliance. Likewise, privacy stipulations—such as those in the EU GDPR—can help businesses protect their customers’ data privacy. Read on for a comparison of GDPR vs HIPAA to learn about the differences and similarities between both frameworks.
If your organization collects, processes, stores, or transmits data that belongs to or concerns residents of European Union (EU) Member States, you are likely subject to the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). One core component of the GDPR is restrictions on retention, which likely necessitates a data retention policy for compliance. Read on to learn how your organization can strategize for and implement such a policy to protect data subjects’ rights.
Does Your Organization Need Privacy by Design Certification?
Privacy by Design certification helps ensure acceptable privacy standards per the European Union’s (EU) General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Although certification is not explicitly a GDPR requirement, the concept of Privacy by Design (PbD) is. What certification achieves is one of the few up-front and tangible methods to demonstrate that protecting data subjects’ personal information is an essential consideration factored throughout systems design, service delivery, and ongoing management. Despite the GDPR’s recent publication, designing IT systems around data privacy is nothing new nor exclusive to the EU’s regulation.
What is a Privacy Impact Assessment Tool for EU GDPR Compliance?
Privacy impact assessment tools serve multiple purposes in IT security. One is compliance with industry and location-based regulations. The EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) exists to identify and minimize risks to personally identifiable information (PII) of EU citizens. It necessitates routine assessments from all entities that interact with EU citizens’ PII. A privacy impact assessment, tool-assisted or otherwise, is one way to ensure GDPR compliance.