All you need is the Internet and the sky’s the limit, or in this case, the cloud. Cloud computing enhances everyday life for families, students, and employees. Even more importantly, it enables smooth operations for businesses in almost every industry. Most people have heard of the cloud in some sense, especially with the widespread use of the Google Suite and Microsoft 365. However, there is so much more to the cloud environment than storing and sharing documents. Are you taking advantage of the many benefits of cloud computing? Continue reading for a comprehensive guide.
What Is Cloud Computing?
The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) defines cloud computing as a model for enabling ubiquitous, convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources (e.g., networks, servers, storage, applications, and services) that can be rapidly provisioned and released with minimal management effort or service provider interaction. Cloud computing attracts users from all different environments because of its versatility and customization ability. The same cloud platform can cater to the needs of students, graphic designers, and web developers all at once. In short, every person uses cloud computing in some form because it offers easy management, storage, processing, and transport of sensitive data. Additionally, the key component to cloud functionality is the Internet, a commodity almost universally available and relatively inexpensive in today’s society.
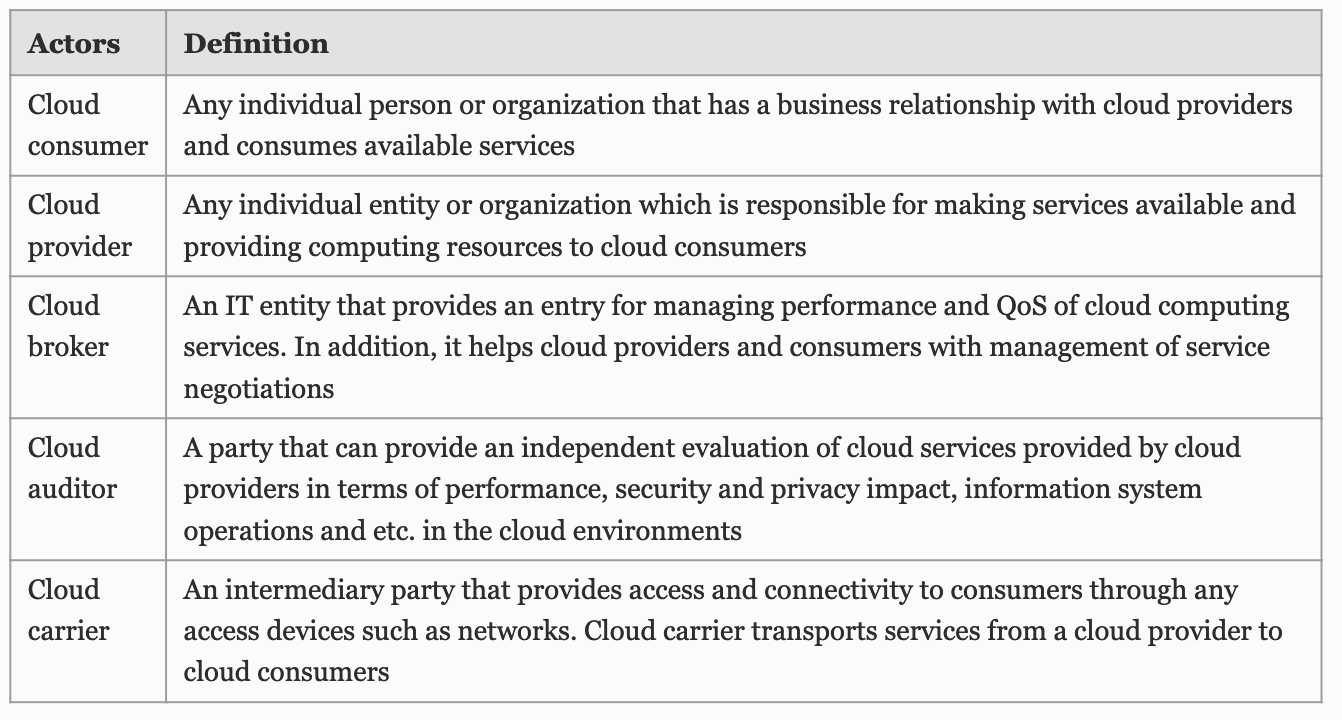
Different Cloud Users:
What Are the Benefits of Cloud Computing?
With such universal applicability, the cloud offers numerous benefits. However, experts generally agree the five benefits below are among the top reasons for using cloud services.
Ease of Access:
Cloud computing offers broad network access anywhere anytime. The type of device an individual uses has no impact on cloud effectiveness. As long as a phone, tablet, or laptop connects to the Internet, the cloud and its subsequent applications are available. The cloud’s ability to store data and documents in a standard format/platform enables widespread usage. This in turn allows for greater collaborative efficiency.
A study found approximately half the workforce operates 2.5 days a week outside the main office. Such statistics underscore how cloud computing allows employees to remain connected while traveling for business, working remotely, or working from home. For example, group conference calls, video calls, and simultaneous document editing improve the productivity and mobility of employees. Subsequently, it can help reduce stress when unforeseen events (e.g., a cold or bad weather) prevent employees from coming into the office.
Assess your cloud security
Reliability:
Cloud computing possesses the potential to offer high reliability — the probability that a system is operational in a time interval without any failures is represented as the system reliability. For example, if a server fails, the host can shift to another available server and quickly re-establish a connection. The data in the cloud remains intact and available with minimal time lost. However, reliability also relies, to an extent, on the user’s Internet service.
When using cloud computing for work, it’s best to invest in a reliable and fast Internet service to maximize cloud benefits. It is worth noting that cloud reliability is not perfect and improving it remains an ongoing challenge. In 2017, Amazon Web Services, GitLab, IBM Cloud Services, and Microsoft Azure all experienced down time, preventing users from accessing data, accounts, etc. Consequently, researchers are constantly looking for new methods to better cloud reliability. A 2018 study proposed a new cloud architecture roadmap [focusing on the What, Where, Which, How, and When of cloud computing] for improving cloud reliability. NIST also provides a detailed Cloud Computing Standards Roadmap with case studies on cloud functionality.
Cost Effective and Efficient:
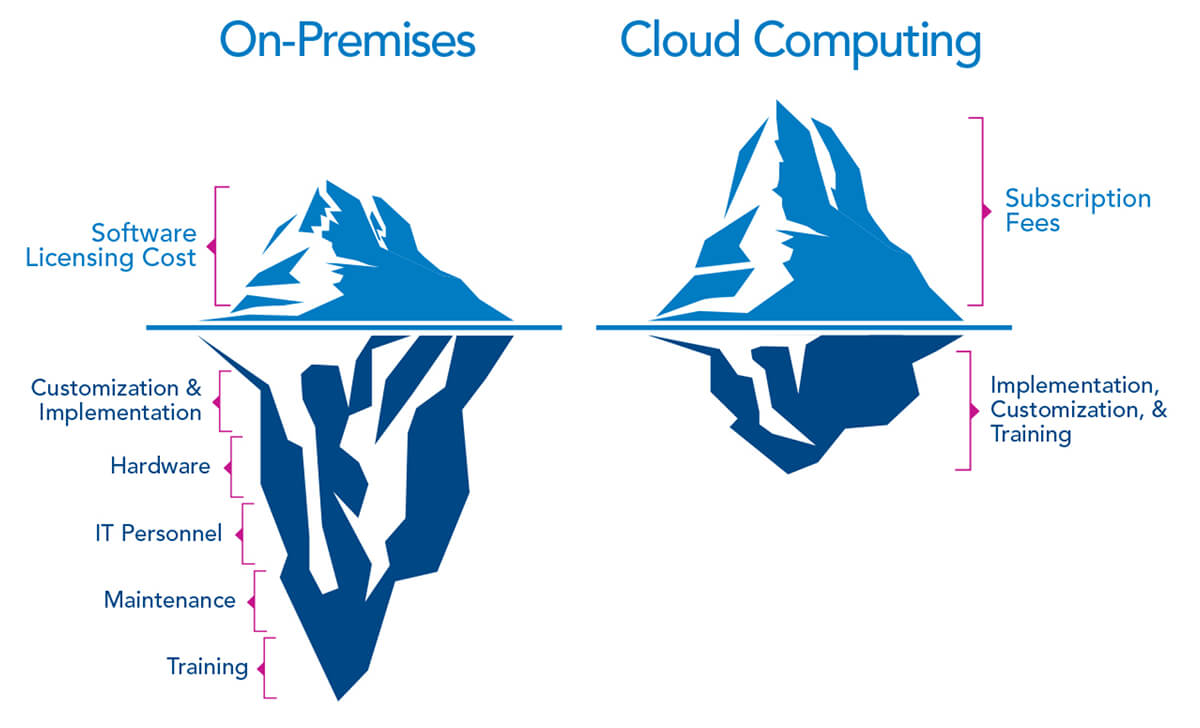
Cloud computing allows users to self-adjust cloud functionality without worrying about the underlying management. Likewise, companies no longer shoulder the burden of constantly updating systems, as the cloud automatically updates. This means less downtime (i.e., for updates) and better allocation of resources. Furthermore, storage space can be expanded without the need to contact a third-party, meaning less hassle and less time wasted on managerial tasks.
Cloud infrastructure reduces the burden on IT departments. Furthermore, the cloud’s virtual environment means less equipment and, therefore, lower maintenance costs. In 2016 alone, cloud computing reduced IT maintenance costs by 16.76 percent. The implementation of cloud computing reduces hardware costs and paper usage all while improving ease of communication. Lastly, cloud venders offer companies the option of purchasing storage in a pay-as-you-go format, meaning less capital is required up front.
Scalability:
Through cloud environments enterprises gain the power to quickly expand or downsize their capacity, allowing for greater elasticity of resources. Enterprises can choose to let third-parties manage their infrastructure (i.e., a managed data center) or utilize a private cloud computing format (where an internal IT team maintains control).
At any time, a company can shift from private to public clouds, or use a combination of clouds (i.e., hybrid cloud). For small businesses in particular, cloud computing offers significant benefits by providing numerous tools and expansion opportunities at a fraction of the cost.
Security Agility:
Cloud computing reduces the recovery time after an attack and allows companies to increase redundancy. In the event that a server goes down, multiple servers are ready to pick up the burden of operations, all in a very short time window. Additionally, less reliance on physical storage means theft or natural disasters cannot cripple businesses on a detrimental level.
Cloud computing requires less internal maintenance (on premise). By migrating to cloud computing, your company will improve efficiency and reduce costs. Source: Kodak
Types of Cloud Computing
The benefits of cloud computing become more evident by understanding the 3 Delivery Models of Cloud Computing:
- SaaS (Software as a Service) grants individuals or entities access to an application or set of applications on a pay-per-use plan. Rather than downloading software on each device, SaaS allows people to access an application via the Internet (i.e., running as a single instance of the software). One platform services many end users. SaaS is most commonly used by society at large. For example, Google’s services (Gmail, Docs, Calendar, etc.) and Microsoft Office 365 provide universal accessibility to students, businesses, and many other institutions. As of Q2 2018, Microsoft led the way in the market share of SaaS revenue, but the vendor market continues to grow at a rapid pace.
- PaaS (Platform as a Service) includes a programming environment, operating system, web server, and database. PaaS creates a virtual ecosystem in which users can design, code, and run programs. Since the vendor manages the underlying infrastructure of the platform, users manage only the applications and data. The primary users of PaaS are developers. Windows Azure, Amazon Web Services, and Heroku are only a few of the many PaaS options available.
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) provides multi-lateral access to four major computing resources: networks, servers, data storage, and virtualization. All activity occurs in a virtual environment. Customers, typically system administrators, take responsibility for application(s), runtime, and middleware while vendors ensure the above four resources function properly. Popular IaaS providers include Amazon Web Services EC2, GOGRID, and Rackspace.
Who’s Using the Cloud?
An IDC report estimated enterprises would allocate half of their IT budgets for cloud computing in 2018 and even more going into 2019. With the cost-effectiveness and efficiency of the cloud, it’s no surprise the integration percentage is on the rise. However, different industries implement cloud services in different ways. Some of the top users of cloud computing include the education, healthcare, and financial industries.
For the education industry, the cloud significantly improves teacher-to-student communication (e.g., distribution of assignments) and student-to-student collaboration (e.g., editing group papers and presentations). For example, email groups give clubs or sports teams the ability to provide information to the entire group in a quick and efficient manner. Even more importantly, it is affordable for schools with limited budgets. The extent of cloud integration for education institutions focuses on SaaS and IaaS.
For healthcare enterprises, cloud services ease the burden of HIPAA compliance. For example, healthcare providers can utilize cloud options to give patients more access to their health information. Furthermore, patients can book appointments online and doctors can provide referrals (e.g., through cloud portals). In a high cost, high traffic industry, the time and cost saving benefits of the cloud should encourage all health institutions to implement more cloud computing in the future.
Financial enterprises utilize cloud computing in many ways. For banks, cloud computing enables automatic transactions and improved customer access (e.g., mobile apps allow for payments). The personal instances the cloud provides for enables safer financial transactions. In large part, the use of the cloud fueled the growth of FinTech — financial technology that seeks to improve and automate the delivery and use of financial services…which has led to the streamlining of wealth management, lending and borrowing, retail banking, fundraising, money transfers/payments. ???The cloud allows FinTech startups to challenge larger monetary institutions without needing significant up-front capital. Financial entrepreneurs can develop and launch new products in a short time frame, allowing them to capitalize on new financial trends, such as the cryptocurrency market. The ability to quickly adapt and scale business models grants cloud-using financial institutions an advantage when attracting and retaining new customers.
In addition to the industries listed above, many other sectors are beginning to take advantage of cloud computing. The entertainment industry utilizes the cloud to deal with high traffic rates on streaming sites. For example, the cloud allowed Netflix to reach a large customer base without falling prey to crashing servers; the scalable nature of the cloud gave Netflix greater agility at a low cost. For the retail industry, the cloud environment increases communication with customers and improves data collection on consumer trends. Large retail companies no longer have to expend large amounts of money on hardware to store sales and inventory data.
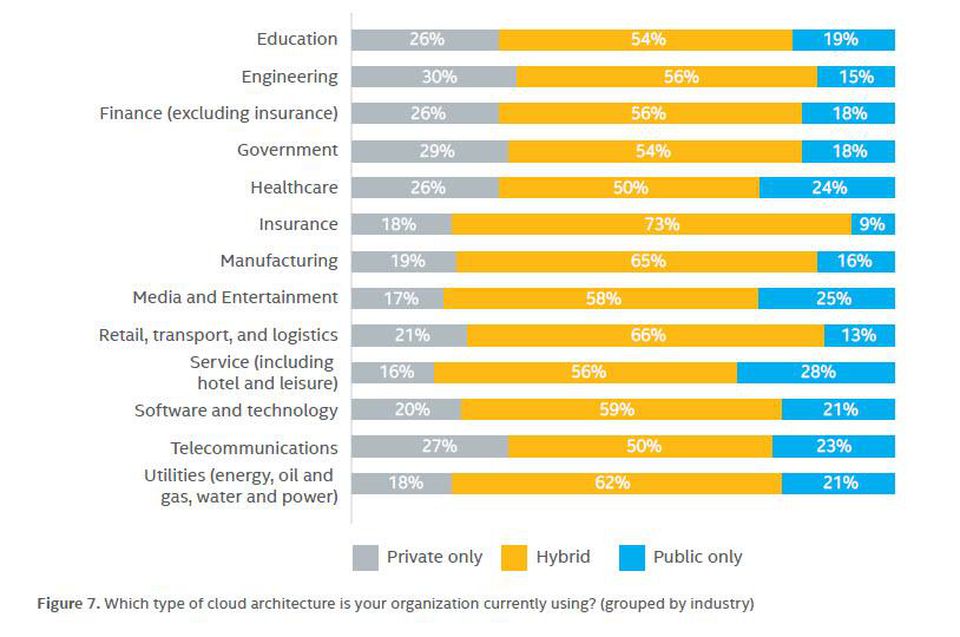
Cloud Usage by Industry 2017 Source: Forbes
Cloud Trends
Even if a company already utilizes cloud computing, new trends and capabilities emerge every year. By 2020, data indicates SaaS use will grow by 18 percent, PaaS will garner 32 percent more investment, and the IaaS market will reach USD 72.4 billion. These increases will affect not only businesses, but also private households. Although still in the development phase, quantum computing in the cloud continues to progress. In 2017, IBM became one of the first companies to make quantum cloud computing available to the public. The benefits of quantum computing range from data encryption to Artificial Intelligence (AI) to complex problem solving. Consequently, experts forecast the quantum computing worth will grow exponentially, reaching USD 8 billion by 2027.
While some companies find it easy to integrate cloud solutions into daily operations, hybrid cloud solutions will likely help the majority of businesses shift more gradually into the cloud computing environment. Hybrid cloud refers to the combination multiple clouds, such as multivendor, private, and public clouds. For example, an enterprise may construct a private cloud compatible with public clouds. While hybrid clouds are not as cost effective, they allow new cloud users to have greater control over the cloud architecture.
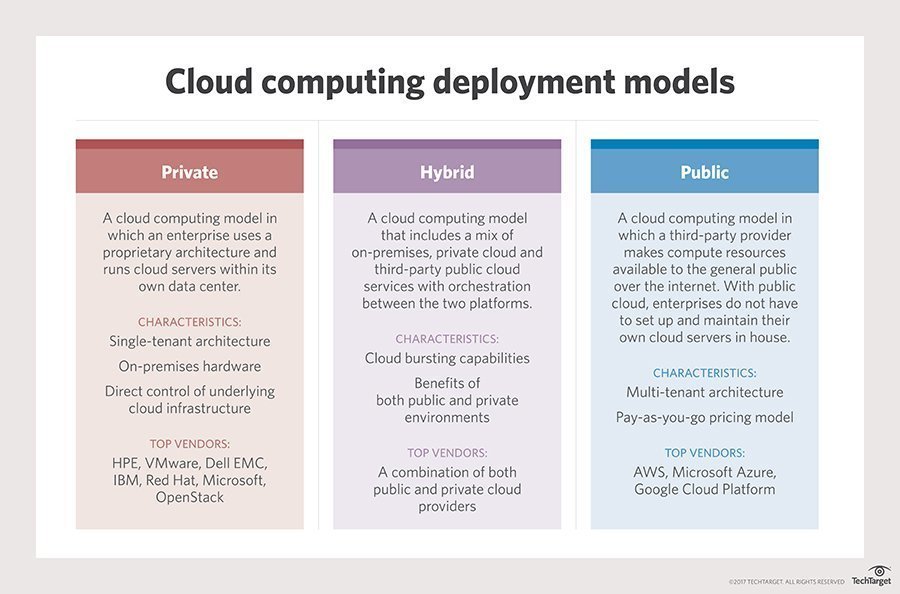
Hybrid cloud computing involves a mix of deployment models. Source: TechTarget
Lastly, cloud security is expected to become more complex, particularly with the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) passed in the European Union. By 2020 an estimated 83 percent of enterprise workloads will take place through the cloud, meaning vulnerabilities to the cloud will become increasingly important to find and patch in a timely manner. The difficulty comes in not only identifying the vulnerabilities in a rapidly developing industry, but also in coordinating the fixes between customers and vendors. Despite these challenges, trust in public cloud-based services increased from 2015-2016, as providers implemented more complex authentication practices.
Need Help Migrating to the Cloud?
As the above trends show, the cloud offers something for everyone, whether an individual, small business, or large corporation. The numerous benefits of cloud computing – like improved efficiency, communication, and resource management — far outweigh the extra time required to research and select the right cloud service. For help developing a cloud architecture for your company or to learn more about cybersecurity solutions, contact RSI Security today.