In this age of digital transformation, the upcoming EU General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) sets a new bar for privacy rights, security, and compliance.
Most companies collect extensive information about their customers, their potential customers, and their employees. The availability of information creates exciting opportunities to reach new customers, to provide existing customers with faster and higher quality services. The opportunities created from information come with a price legal risks, challenges, and uncertainty. Protecting valuable information poses an increasingly difficult challenge in light of ever changing cyber-threats. When information does become breached, companies often find themselves the target of government investigations and private litigation.
Heres an overview of GDPR compliance and privacy data security.
Goal: The aim of the GDPR is to protect all EU citizens from privacy and data breaches. GDPR regulatory requirements applies to all companies processing the personal data of data subjects residing in the Union, regardless of the companys location.
Personal data according to GDPR:
“personal data” shall mean any information relating to an identified or identifiable natural person (‘Data Subject’); an identifiable person is one who can be identified, directly or indirectly, in particular by reference to an identification number or to one or more factors specific to his physical, physiological, mental, economic, cultural or social identity”.
North American Organizations are familiar with Personally Identifiable Information (PII), that refers to a relatively narrow range of personal data such as name, address, birth date, Social Security number and financial information such as credit card numbers or bank accounts. Personal data, in the context of GDPR, covers a much wider range of information. In other words, all PII is personal data but not all personal data is PII.
Personal data in scope of the regulation can include, but is not limited to, the following:
- Name
- Identification number
- Email address
- Online user identifier
- Social media posts
- Physical, physiological, or genetic information
- Medical information
- Location
- Bank details
- IP address
- Cookies
View our GDPR infographic here
Does GDPR apply to your organization?
The diagram below will help you determine the applicability.
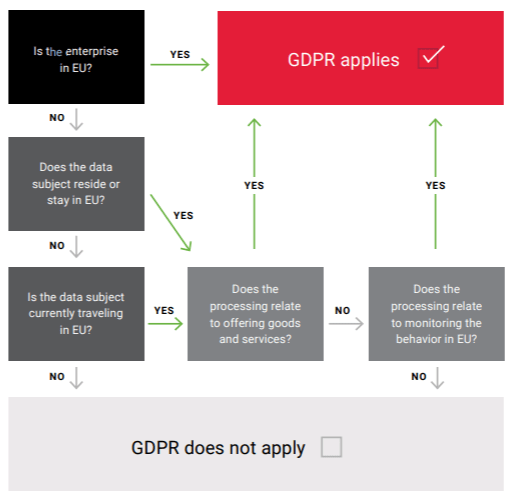
GDPR regulation is described in 11 chapters and 99 articles. Here are a few highlights.
- Article 25 Data protection by design and default: Control exposure to personal data.
- Article 32Security of processing: Security mechanisms to protect personal data. – Employ pseudonymization and encryption.
- Article 33Notification of a personal data breach to the supervisory authority – Detect & notify data breach within 72 hours
- Article 30Records of processing activities: Log and monitor operations.
- Article 35Data protection impact assessment: Document risks and security measures.
What can you do to protect personal data and become GDPR compliant?
GDPR compliance requires a holistic approach across the entire enterprise because personal data may reside across many organizational silos.
Perform Risk Assessment
A formal process used by organizations to identify threats and vulnerabilities that could negatively impact the security of personal data. Organizational resources can be effectively allocated to implement controls that reduce the likelihood and/or the potential impact of the threats being realized.
Discover
Understand how personal data is used and accessed within the organization; Identify what personal data is captured, stored, processed, transmitted, shared and where it resides.
Manage and Protect
By following the GDPR regulation guidelines, You can take a number of steps to minimize the risk of personal data breach. Minimize the use, collection, and retention of personal data. if you dont need it, dont store it. By limiting personal data collections to the least amount necessary to conduct its mission, the organization may limit potential negative consequences in the event of a data breach involving personal data.
Anonymize data and use Pseudonyms
Basically make it impossible or difficult to access and identify the data subject from the data elements. Full data records are not always necessary, such as for some forms of research, resource planning, and examinations of correlations and trends. For example, remove account numbers, names, ids, and any other identifiable information from a set of financial records.
Article 26 of the GDPR defines anonymized data as data rendered anonymous in such a way that the data subject is not or no longer identifiable.
By contrast, Article 4(5) of the GDPR defines pseudonymization as the processing of personal data in such a way that the data can no longer be attributed to a specific data subject without the use of additional information.
Establish security controls to protect personal data and reduce the risk of data breaches. Secure your systems that capture, process and share personal data. Establish controls to process and approve data requests. Implement strong access control measures that only allows authenticated and authorized individuals and systems to access the data elements on a need-to-know basis. Use secure methods and encryption when transmitting personal data.
Maintain Security Awareness
Establish continuous security awareness among the employees and partners so that everyone abides by the organizational security governance policies, stays vigilant to data access violations and data breach incidents.
Monitor and Detect
Establish processes and configure systems to monitor activities that capture, store, transmit and access personal data. Implement controls to detect attempts to access or unauthorized access to the personal data.
Respond and Recover
Establish an incident response program where the organization teams are prepared to deal with adverse events and data breach. Notify the authorities within 72 hours of data breach identification. Organizations should develop additional policies, such as determining when and how individuals should be notified, when and if a breach should be reported publicly.
Perform periodic risk and security assessments, and have a GDPR consultant test your security controls and incident response plans.
RSI Securitys GDPR consultant professionals will expertly guide you through our GDPR compliance program that is optimized for your identified gaps.
Sources:
https://www.eugdpr.org/
http://www.isaca.org/info/gdpr/index.html
https://www.nist.gov/cyberframework
About RSI Security
RSI is the nation’s premier information security and compliance provider dedicated to helping organizations achieve risk-management success. We work with some of the world’s leading companies, institution and governments to ensure the safety of their information and their compliance with applicable regulation. We also are a security and compliance software ISV and stay at the forefront of innovative tools to save assessment time, increase compliance and provide additional safeguard assurance. With a unique blend of software based automation and managed services, RSI can assist all sizes of organizations in managing IT governance, Risk management and compliance efforts (GRC).




